Logstash Basic - Plugins
Logstash Basic & Plugins
Logstash 简介
输入、过滤器和输出:
Logstash 能够动态地采集、转换和传输数据,不受格式或复杂度的影响。利用 Grok 从非结构化数据中派生出结构,从 IP 地址解码出地理坐标,匿名化或排除敏感字段,并简化整体处理过程。
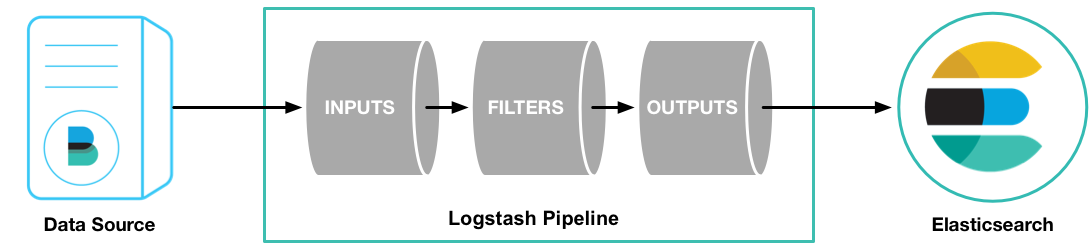
官方图文并茂简介:https://www.elastic.co/cn/logstash
插件离线管理
插件打包
确保要打包的所有插件都已安装在登台服务器上,并且该登台服务器可以访问Internet。
运行bin/logstash-plugin prepare-offline-pack子命令来打包插件和依赖项:
# bin/logstash-plugin prepare-offline-pack --output OUTPUT --overwrite [PLUGINS]
# 打包Beats输入插件和所有依赖项bin/logstash-plugin prepare-offline-pack logstash-input-beats# 使用通配符打包所有过滤器插件和所有依赖项bin/logstash-plugin prepare-offline-pack logstash-filter-*# 打包所有过滤器插件,Beats输入插件以及所有依赖项bin/logstash-plugin prepare-offline-pack logstash-filter-* logstash-input-beats插件安装
Windows example:
bin/logstash-plugin install file:///c:/path/to/logstash-offline-plugins-7.7.1.zipLinux example:
bin/logstash-plugin install file:///path/to/logstash-offline-plugins-7.7.1.zip插件升级
# 升级所有bin/logstash-plugin updatebin/logstash-plugin update logstash-output-kafka更多参考:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/offline-plugins.html#_updating_offline_plugins
插件移除
bin/logstash-plugin remove logstash-output-kafkaInput Plugins
让 logstash 可以读取特定的事件源, 事件源可以是从stdin屏幕输入读取,可以从file指定的文件,也可以从es,filebeat,kafka,redis等读取。
stadin:从标准输入读取file:从文件读取数据
file{ path => ['/var/log/nginx/access.log'] # 要输入的文件路径 type => 'nginx_access_log' start_position => "beginning"}# path 可以用/var/log/*.log,/var/log/**/*.log,如果是/var/log则是/var/log/*.log# type 通用选项. 用于激活过滤器# start_position 选择logstash开始读取文件的位置,begining或者end。# 还有一些常用的例如:discover_interval,exclude,sincedb_path,sincedb_write_interval等可以参考官网syslog: 通过网络将系统日志消息读取为事件
syslog{ port =>"514" type => "syslog"}# port 指定监听端口(同时建立TCP/UDP的514端口的监听)
#从syslogs读取需要实现配置rsyslog:# cat /etc/rsyslog.conf 加入一行# ------------------------------*.* @172.17.128.200:514 #指定日志输入到这个端口,然后logstash监听这个端口,如果有新日志输入则读取# service rsyslog restart #重启日志服务beats:从 Elastic beats 获取事件
beats { port => 5044 #要监听的端口 client_inactivity_timeout => 600 ssl => true ssl_certificate_authorities => ["/home/work/certificate/chain-ca.pem"] ssl_certificate => "/home/work/certificate/server.crt.pem" ssl_key => "/home/work/certificate/server.key.pem" ssl_verify_mode => "force_peer"}# 还有host等选项
# 从beat读取需要先配置beat端,从beat输出到logstash。# vim /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml# ------------------------output.logstash:hosts: ["localhost:5044"]Kafka:将 kafka topic 中的数据读取为事件
kafka{ bootstrap_servers=> "kafka01:9092,kafka02:9092,kafka03:9092" topics => ["access_log"] group_id => "logstash-file" codec => "json"}
kafka{ bootstrap_servers=> "kafka01:9092,kafka02:9092,kafka03:9092" topics => ["weixin_log","user_log"] codec => "json"}
# bootstrap_servers 用于建立群集初始连接的Kafka实例的URL列表。# topics 要订阅的主题列表,kafka topics# group_id 消费者所属组的标识符,默认为logstash。kafka中一个主题的消息将通过相同的方式分发到Logstash的group_id# codec 通用选项,用于输入数据的编解码器。更多插件:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/input-plugins.html
Filter Plugins
数据从源传输到存储库的过程中,Logstash 过滤器能够解析各个事件,识别已命名的字段以构建结构,并将它们转换成通用格式,以便进行更强大的分析和实现商业价值。
需要注意的是,对于filter.conf配置是可以热加载的,如果时间格式配置错误,会导致logstash进程挂掉,对于问题的排查,可以自行查询logstash的日志。
grok:解析文本并构造 ,把非结构化日志数据通过正则解析成结构化和可查询化
grok { match => {"message"=>"^%{IPORHOST:clientip} %{USER:ident} %{USER:auth} \[%{HTTPDATE:timestamp}\]" %{WORD:verb} %{DATA:request} HTTP/%{NUMBER:httpversion} "%{NUMBER:response:int} (?:-|%{NUMBER:bytes:int}) %{QS:referrer} %{QS:agent}$"} }# 匹配nginx日志# 203.202.254.16 - - [22/Jun/2018:16:12:54 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 3700 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_11_6) AppleWebKit/601.7.7 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/9.1.2 Safari/601.7.7"#220.181.18.96 - - [13/Jun/2015:21:14:28 +0000] "GET /blog/geekery/xvfb-firefox.html HTTP/1.1" 200 10975 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Baiduspider/2.0; +http://www.baidu.com/search/spider.html)"
# 注意这里grok 可以有多个match匹配规则,如果前面的匹配失败可以使用后面的继续匹配。例如grok { match => ["message", "%{IP:clientip} - %{USER:user} \[%{HTTPDATE:raw_datetime}\] \"(?:%{WORD:verb} %{URIPATHPARAM:request} HTTP/%{NUMBER:httpversion})\" (?:\"%{DATA:body}\" )?(?:\"%{DATA:cookie}\" )?%{NUMBER:response} (?:%{NUMBER:bytes:int}|-) \"%{DATA:referrer}\" \"%{DATA:agent}\" (?:(%{IP:proxy},? ?)*|-|unknown) (?:%{DATA:upstream_addr} |)%{NUMBER:request_time:float} (?:%{NUMBER:upstream_time:float}|-)"] match => ["message", "%{IP:clientip} - %{USER:user} \[%{HTTPDATE:raw_datetime}\] \"(?:%{WORD:verb} %{URI:request} HTTP/%{NUMBER:httpversion})\" (?:\"%{DATA:body}\" )?(?:\"%{DATA:cookie}\" )?%{NUMBER:response} (?:%{NUMBER:bytes:int}|-) \"%{DATA:referrer}\" \"%{DATA:agent}\" (?:(%{IP:proxy},? ?)*|-|unknown) (?:%{DATA:upstream_addr} |)%{NUMBER:request_time:float} (?:%{NUMBER:upstream_time:float}|-)"]}date:日期解析 解析字段中的日期,然后转存到***@timestamp***
grok{ match => {"message"=>"%{DATA:raw_datetime}"}}date{ match => ["raw_datetime","YYYY-MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS"] remove_field =>["raw_datetime"]}
#将raw_datetime存到@timestamp 然后删除raw_datetime
#24/Jul/2018:18:15:05 +0800date { match => ["timestamp","dd/MMM/YYYY:HH:mm:ss Z]}mutate:对字段做处理 重命名、删除、替换和修改字段
filter { mutate { split => ["hostname", "."] add_field => { "shortHostname" => "%{hostname[0]}" } }
mutate { rename => ["shortHostname", "hostname" ] }}mutate.covert:类型转换类型包括:integer,float,integer_eu,float_eu,string和boolean
filter{ mutate{# covert => ["response","integer","bytes","float"] #数组的类型转换 convert => {"message"=>"integer"} }}#测试------->{ "host" => "localhost", "message" => 123, #没带“”,int类型 "@timestamp" => 2018-06-26T02:51:08.651Z, "@version" => "1"}mutate.split:使用分隔符把字符串分割成数组
mutate{ split => {"message"=>","}}#---------->aaa,bbb{ "@timestamp" => 2018-06-26T02:40:19.678Z, "@version" => "1", "host" => "localhost", "message" => [ [0] "aaa", [1] "bbb" ]}192,128,1,100{ "host" => "localhost", "message" => [ [0] "192", [1] "128", [2] "1", [3] "100" ], "@timestamp" => 2018-06-26T02:45:17.877Z, "@version" => "1"}mutate.merge: 合并字段 。数组和字符串 ,字符串和字符串
filter{ mutate{ add_field => {"field1"=>"value1"} } mutate{ split => {"message"=>"."} #把message字段按照.分割 } mutate{ merge => {"message"=>"field1"} #将filed1字段加入到message字段 }}#--------------->abc{ "message" => [ [0] "abc," [1] "value1" ], "@timestamp" => 2018-06-26T03:38:57.114Z, "field1" => "value1", "@version" => "1", "host" => "localhost"}
abc,.123{ "message" => [ [0] "abc,", [1] "123", [2] "value1" ], "@timestamp" => 2018-06-26T03:38:57.114Z, "field1" => "value1", "@version" => "1", "host" => "localhost"}mutate.rename: 对字段重命名
filter{ mutate{ rename => {"message"=>"info"} }}#-------->{ "@timestamp" => 2018-06-26T02:56:00.189Z, "info" => "123", "@version" => "1", "host" => "localhost"}remove_field:移除字段join:用分隔符连接数组,如果不是数组则不做处理
mutate{ split => {"message"=>":"}}mutate{ join => {"message"=>","}}------>abc:123{ "@timestamp" => 2018-06-26T03:55:41.426Z, "message" => "abc,123", "host" => "localhost", "@version" => "1"}aa:cc{ "@timestamp" => 2018-06-26T03:55:47.501Z, "message" => "aa,cc", "host" => "localhost", "@version" => "1"}gsub:用正则或者字符串替换字段值。仅对字符串有效
mutate{ gsub => ["message","/","_"] #用_替换/ }
------>a/b/c/{ "@version" => "1", "message" => "a_b_c_", "host" => "localhost", "@timestamp" => 2018-06-26T06:20:10.811Z}update:更新字段。如果字段不存在,则不做处理
mutate{ add_field => {"field1"=>"value1"} } mutate{ update => {"field1"=>"v1"} update => {"field2"=>"v2"} #field2不存在 不做处理 }---------------->{ "@timestamp" => 2018-06-26T06:26:28.870Z, "field1" => "v1", "host" => "localhost", "@version" => "1", "message" => "a"}replace:更新字段。如果字段不存在,则创建
mutate{ add_field => {"field1"=>"value1"} } mutate{ replace => {"field1"=>"v1"} replace => {"field2"=>"v2"} }---------------------->{ "message" => "1", "host" => "localhost", "@timestamp" => 2018-06-26T06:28:09.915Z, "field2" => "v2", #field2不存在,则新建 "@version" => "1", "field1" => "v1"}geoip:根据来自Maxmind GeoLite2数据库的数据添加有关IP地址的地理位置的信息
geoip { source => "clientip" database =>"/tmp/GeoLiteCity.dat" }ruby:ruby插件可以执行任意Ruby代码
urldecode:用于解码被编码的字段,可以解决URL中 中文乱码的问题
urldecode{ field => "message" }
# field :指定urldecode过滤器要转码的字段,默认值是"message"# charset(缺省): 指定过滤器使用的编码.默认UTF-8kv:通过指定分隔符将字符串分割成key/value
kv{ prefix => "url_" #给分割后的key加前缀 target => "url_ags" #将分割后的key-value放入指定字段 source => "message" #要分割的字段 field_split => "&" #指定分隔符 remove_field => "message" }-------------------------->a=1&b=2&c=3{ "host" => "localhost", "url_ags" => { "url_c" => "3", "url_a" => "1", "url_b" => "2" }, "@version" => "1", "@timestamp" => 2018-06-26T07:07:24.557Zuseragent:添加有关用户代理(如系列,操作系统,版本和设备)的信息
if [agent] != "-" { useragent { source => "agent" target => "ua" remove_field => "agent" }}# if语句,只有在agent字段不为空时才会使用该插件#source 为必填设置,目标字段#target 将useragent信息配置到ua字段中。如果不指定将存储在根目录中更多插件:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/filter-plugins.html
Codec Plugins
codec 本质上是流过滤器,可以作为input 或output 插件的一部分运行。
multiline codec plugin:多行合并, 处理堆栈日志或者其他带有换行符日志需要用到
input { stdin { codec => multiline { pattern => "pattern, a regexp" #正则匹配规则,匹配到的内容按照下面两个参数处理 negate => "true" or "false" # 默认为false。处理匹配符合正则规则的行。如果为true,处理不匹配符合正则规则的行。 what => "previous" or "next" #指定上下文。将指定的行是合并到上一行或者下一行。 } }}codec => multiline { pattern => "^\s" what => "previous"}# 以空格开头的行都合并到上一行
codec => multiline { # Grok pattern names are valid! :) pattern => "^%{TIMESTAMP_ISO8601} " negate => true what => "previous"}# 任何不以这个时间戳格式开头的行都与上一行合并
codec => multiline { pattern => "\\$" what => "next"}# 以反斜杠结尾的行都与下一行合并更多插件:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/codec-plugins.html
Output Plugins
将事件发送到特定目标。
stdout:标准输出。将事件输出到屏幕上
output{ stdout{ codec => "rubydebug" }}file:将事件写入文件
file { path => "/data/logstash/%{host}/{application} codec => line { format => "%{message}"} } }kafka:将事件发送到kafka
kafka{ bootstrap_servers => "localhost:9092" topic_id => "test_topic" #必需的设置。生成消息的主题 }elasticseach:在es中存储日志
elasticsearch { hosts => "localhost:9200" index => "nginx-access-log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" }#index 事件写入的索引。可以按照日志来创建索引,以便于删旧数据和按时间来搜索日志email:输出到邮箱
output { if "shouldmail" in [tags] { email { to => 'technical@example.com' from => 'monitor@example.com' subject => 'Alert - %{title}' body => "Tags: %{tags}\\n\\Content:\\n%{message}" template_file => "/tmp/email_template.mustache" domain => 'mail.example.com' port => 25 } }}更多插件:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/current/output-plugins.html
